A very common problem is when people come to me with cards (SD Cards, Compact Flash Cards) ,see pic below, from cameras where photos are missing. The same problems can occur with USB or flash drives and Micro SD cards from mobile phones.



Fat File System
The file allocation table (FAT) file system was originally designed for small disks and simple folder structures. The file allocation tables and the root folder are stored in a fixed location on a drive so that the files needed to start the system are easily located.
Structure of a FAT Volume
The Partition Boot Sector
The first sector on a drive is called Master Boot Record and it uses the Partition Boot Sector on the system partition to load the operating system kernel files. On the type of drives we are talking about Micro SD Cards, USB or Flash Drives and Camera Memory Cards there is usually only one partition and the Master Boot Record uses the PBS to find this partition.
File Allocation Table
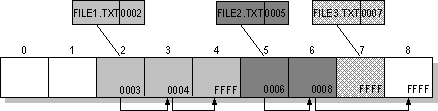
We can see from the above image two copies of the file allocation table are kept, in case one becomes damaged. The tables are always stored in a fixed location so that the files needed to start the system can be correctly located. The file allocation table contains the following types of information about each cluster on the volume
- Unused (0x0000)
- Cluster in use by a file
- Bad cluster (0xFFF7)
- Last cluster in a file (0xFFF8-0xFFFF)
There is no organization to the FAT folder structure, and files are given the first available location in the area marked other files and folders in the above diagram,
If we look at the diagram below the FAT contains a linked list of where the the information for a file exist on the SD Card or USB drive.
FAT Root Folder
The root folder contains an entry for each file and folder on the root. The only difference between the root folder and other folders is that the root folder is on a specified location on the disk and has a fixed size (512 entries for a hard disk, number of entries on a floppy disk depends on the size of the disk).
Folders have a set of 32-byte Folder Entries for each file and subfolder contained in the folder (see example figure below). The Folder Entry includes the following information:
the Fat Root Folder plays a crucial role in storing and organizing information. With attributes byte providing 8 bits worth of essential details, such as read-only, hidden, system file, volume label, subdirectory, archive status and more; the create time (24 bits), create date (16 bits), last access date (16 bits), last modified time (16 bits), and last modified date (16 bits) capture the timeline of when files were created or altered. Furthermore, the starting cluster number in the file allocation table (16 bits) dictates where in memory to locate specific files for quick retrieval. Lastly, the file size is detailed using 32-bits to accurately measure how much space each document occupies within the storage system. Such meticulous organization ensures efficient data management and accessibility for users across various platforms.
Fat File System Common Errors
The file or directory is corrupted and unreadable
The Drive is not formatted.
Directory Structure exists but is unreadable.
It is very common for these sorts of errors
For more information on camera card data recovery
REQUEST A QUOTE
Address
126 Whatley Crescent Maylands
call:(08) 6180 6959
126 Whatley Crescent
6 Days a week from 8:00am - 5:00pm
