The following are the most popular freeware utilities
1 Ext2Fsd
Ext2Fsd is a Windows file system driver for the Ext2, Ext3, and Ext4 file systems. It allows Windows to read Linux file systems natively, providing access to the file system via a drive letter that any program can access.
2 DiskInternals Linux Reader
Linux Reader is a freeware application from DiskInternals, developers of data recovery software. In addition to the Ext file systems, Linux Reader also supports ReiserFS and Apple’s HFS and HFS+ file systems. It’s read-only, so it can’t damage your Linux file system.
3 Ext2explore
Is an open-source application that works similarly to DiskInternals Linux Reader—but only for Ext4, Ext3, and Ext2 partitions.
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
The problem with all of these utilities is that typically when installing a Linux distribution the drive is partitioned using Logical Volume Manager. I have talked about LVM in a Previous post .Data Recovery
LVM allows for very flexible disk space management. It provides features like the ability to add disk space to a logical volume and its filesystem while that filesystem is mounted and active and it allows for the collection of multiple physical hard drives and partitions into a single volume group which can then be divided into logical volumes. This performs the same function as Windows Disk Manager.
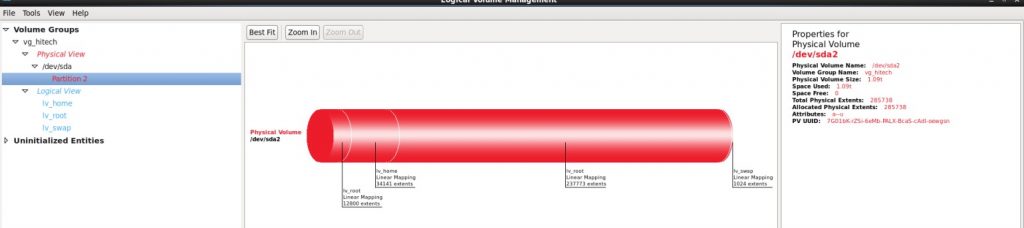
When installing Linux a typical drive layout will be created with the following partitions. As seen in the image below.
Boot
Home
Root
Typical Linux System LVM drive divided into 3 partitions
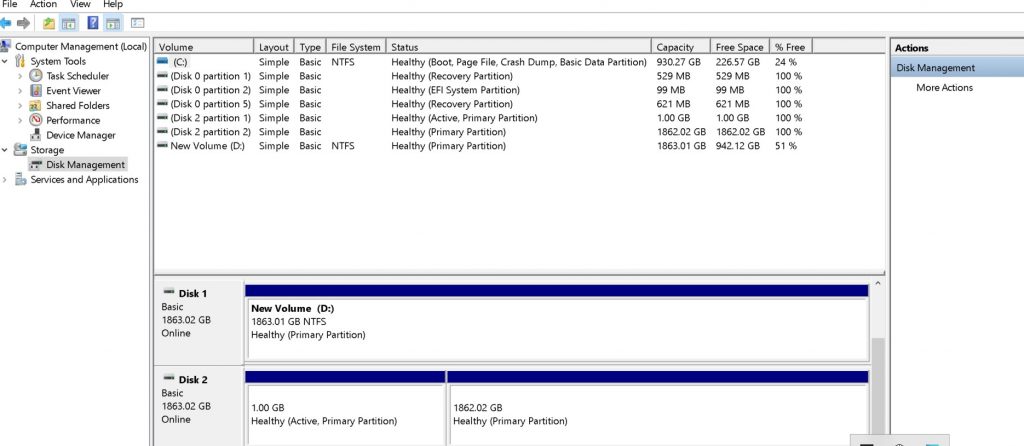
Linux drive viewed in Windows Disk Management
Here in the snapshot below I have removed the Linux drive from it’s case and and attached the drive to a Windows System and the snapshot displays that the drive’s partitions are not recognised by Disk Manager. See DISK 2.
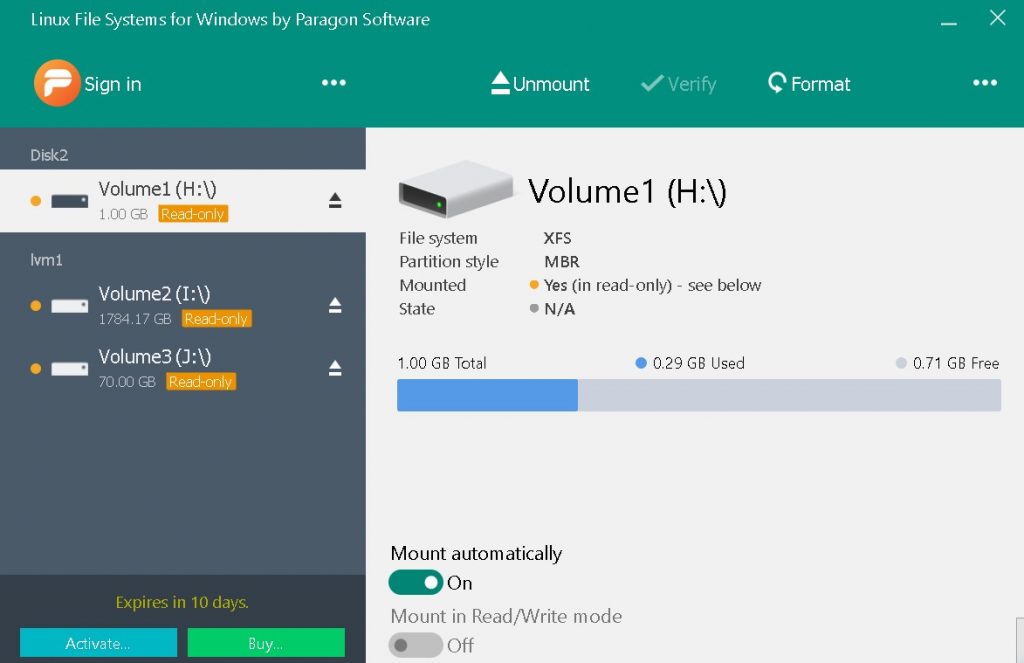
Linux File System for Windows Paragon
Linux file system for windows allows access to drives configured with Logical Volume Manager and access to partitions formatted with Ext2 , Ext3 and Ext4.
The picture below is the initial screen displayed after installation. I am using the trial version of the software.
Linux File System for Windows Features
Automount eXT2 , eXT3 & eXT4 volumes are automatically mounted at startup, for ease each time you restart the operating system or power your computer on. You can disable this.
Write Access When ExtFS volume is mounted in write mode, you can do everything with files and folders it contains: read, edit, delete, rename, create new.
Volume Administration Formats, checks integrity, and repairs corrupted ExtFS volumes with minimal effort.
Read/write support for LVM (Logical Volume Management) With Linux File Systems for Windows, your Linux’s logical volume manager won’t lose any of its functions: it will be able to perform open, close, read and write operations and, in general, operate in a usual way.
Command Line Interface Get full control over Linux File Systems for Windows by Paragon Software via a command line.
Boot Partition
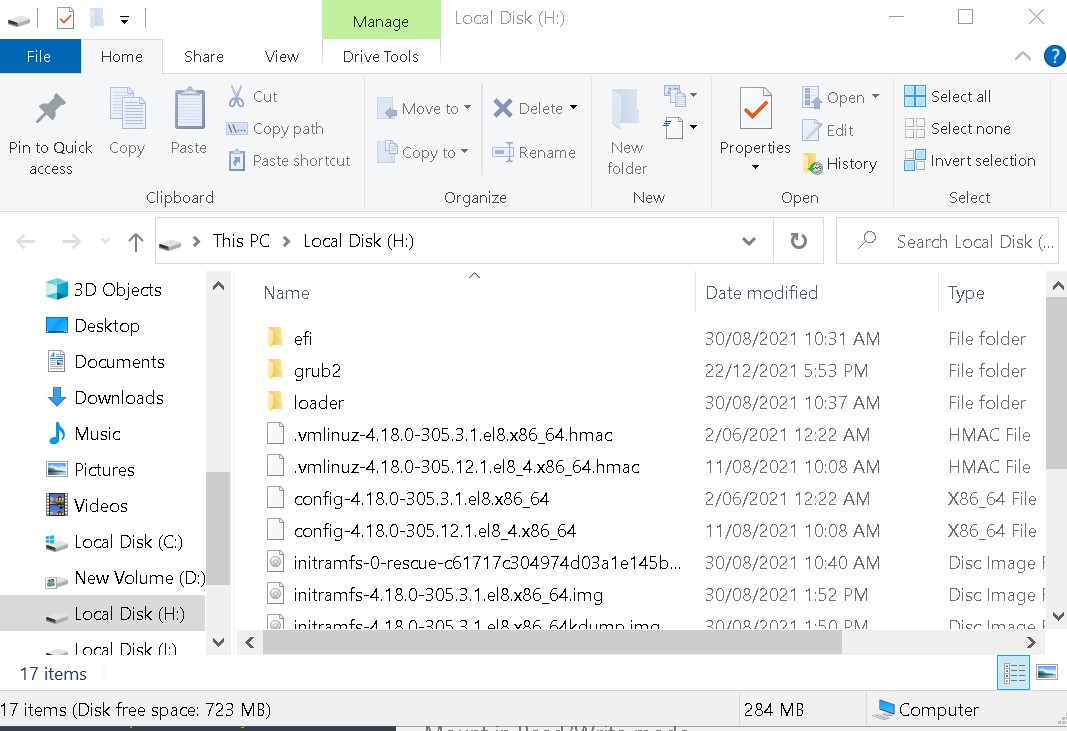
Home Partition
The home partition is where you will find your user data eg the desktop , documents , pictures and downloads. See snapshot below of the Home partition of a 2TB drives with Centos 7 installed.
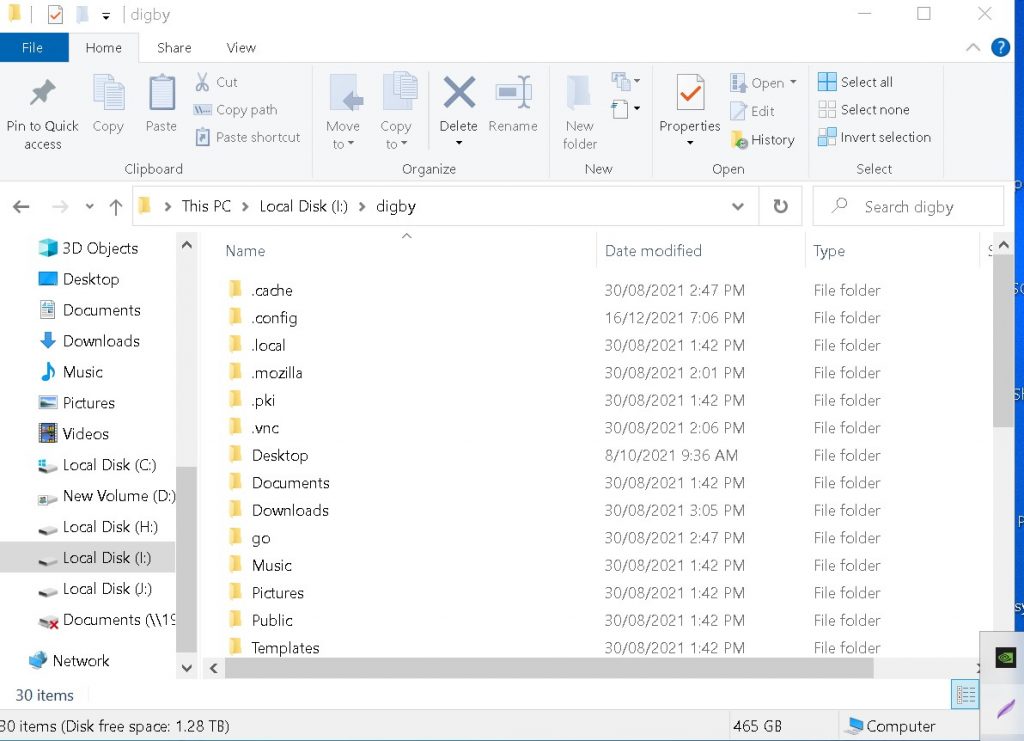
Root Partition
The root partition is where all the Linux operating system files are maintained . See Snapshot below of a Centos 7 root partiton.